This website was created as a project for Genetics 677, an undergraduate course at UW Madison.
Phylogeny trees for WRN protein homologs
Analysis
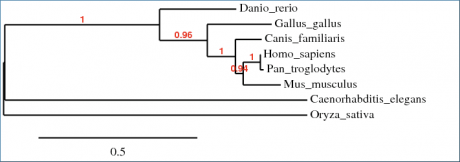
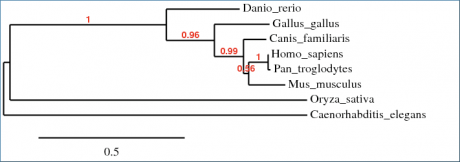
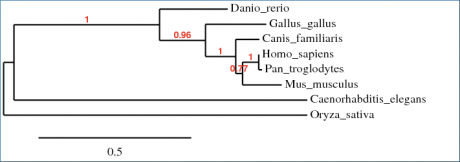
Phylogeny trees are a tool used to compare evolutionary relatedness among a group of species. In this instance, a program called Phylogeny.fr was used to align amino acid sequences of WRN homologues into a phylogenetic tree. Three different algorithms were used to make the comparisons. Overall, there was a very close agreement among phylogeny trees, with only minor variations in branch distance. These differences most likely arise from the matrices used to organize the trees rather than the alignments themselves. The only other difference among the phylogeny trees was that in Figure 2, the ClustalW algorithm revealed that the hypothetical protein O. sativa was slightly more related to the H. sapiens WRN protein than the C. elegans homologue; whereas in the other two algorithms (Fig. 1,3) this relationship was reversed. This is unsurprising, as the protein homology alignments completed by BLAST found that C. elegans and O. sativa differed from each other by only 3% in comparison to H. sapiens WRN protein.
Figure 1. This phylogeny tree was generated by Phylogeny.fr using the MUSCLE algorithm and organized by maxmimum likelihood.
Figure 2. This phylogeny tree was generated by Phylogeny.fr using the ClustalW algorithm and organized by maximum likelihood.
Figure 3. This phylogeny tree was generated by Phylogeny.fr using the T-COFFEE algorithm and organized by maximum likelihood.
References
1. (Title Figure) Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Retrieved March 18, 2010 from http://www.phylogeny.fr/version2_cgi/index.cgi
2. (Figures 1,2,3) Phylogeny.fr. Marseille, France: Marseille-Nice Genopole; June 2009. Available from: http://www.phylogeny.fr/version2_cgi/index.cgi
2. (Figures 1,2,3) Phylogeny.fr. Marseille, France: Marseille-Nice Genopole; June 2009. Available from: http://www.phylogeny.fr/version2_cgi/index.cgi